
When it comes to clothing customization, one of the most tricky problems for lots of clients in clothing industry have ever met is printings. The printings can make a big influence on their designs, however, sometimes they encounter some problems such as inevitable damages to fabrics, or may be easily faded by multiple washing. The difficulties of hoosing printings are affected by multiple factors, such as fabrics, patterns' sizes and material, printing equipment or dyeing methods. Thus, here is a suggestion: before making a decision on printings, except your logos or patterns designs, you should learn more details of your using fabrics, materials, dyeing so that we can learn whether your choosing printings are suitable for your designs or not.
Back to our theme today, it is also important to understand more pros and cons of different printings during customization while you start designing your own activewear or athleisure, especially before bulk orders. Thus, Arabella team here to update you some common printings that you might meet in the following to assist you to make a better choice. Hope it would help.
1. Direct-to-Garment (DTG) Printing
How it works:
Inkjet-like printers spray eco-friendly inks directly onto fabric, guided by digital designs. No screens or plates required.
Pros:
Perfect for small batches, photo-realistic details, and fast turnarounds. Eco-friendly with minimal waste.
Cons:
Slow for bulk orders, costly equipment / inks, and limited fabric compatibility (some require pre-treatment).
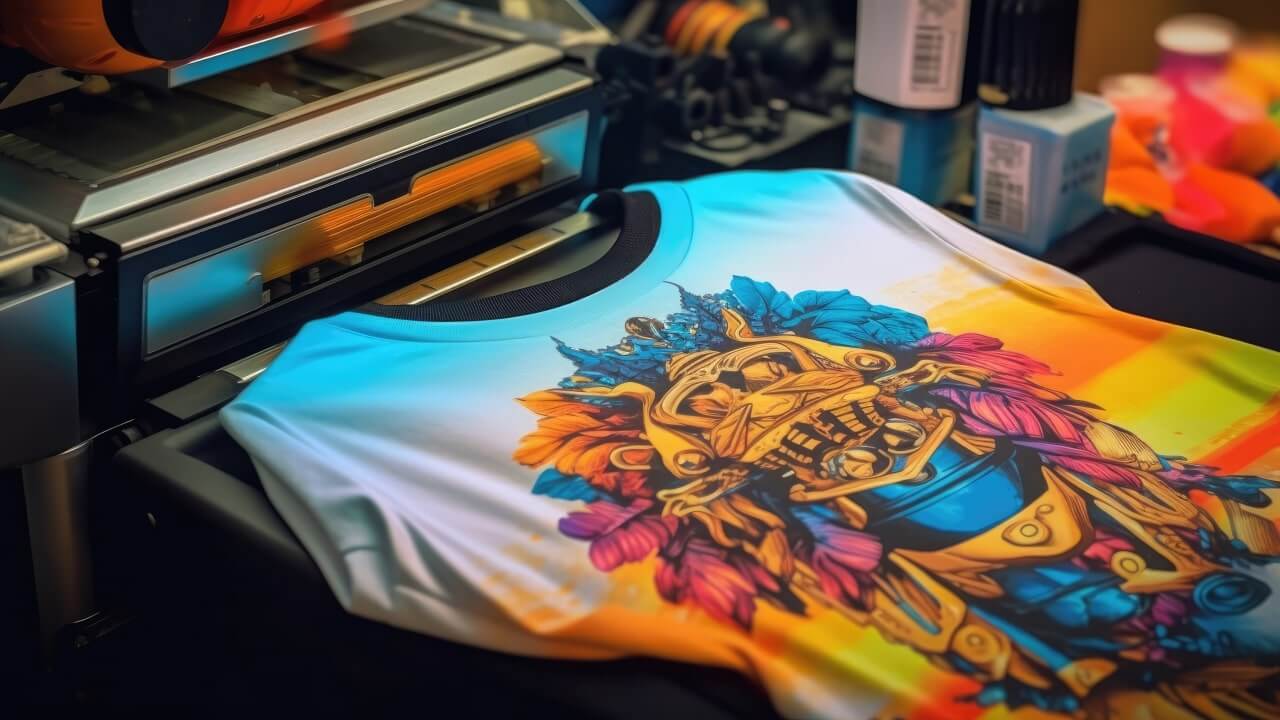
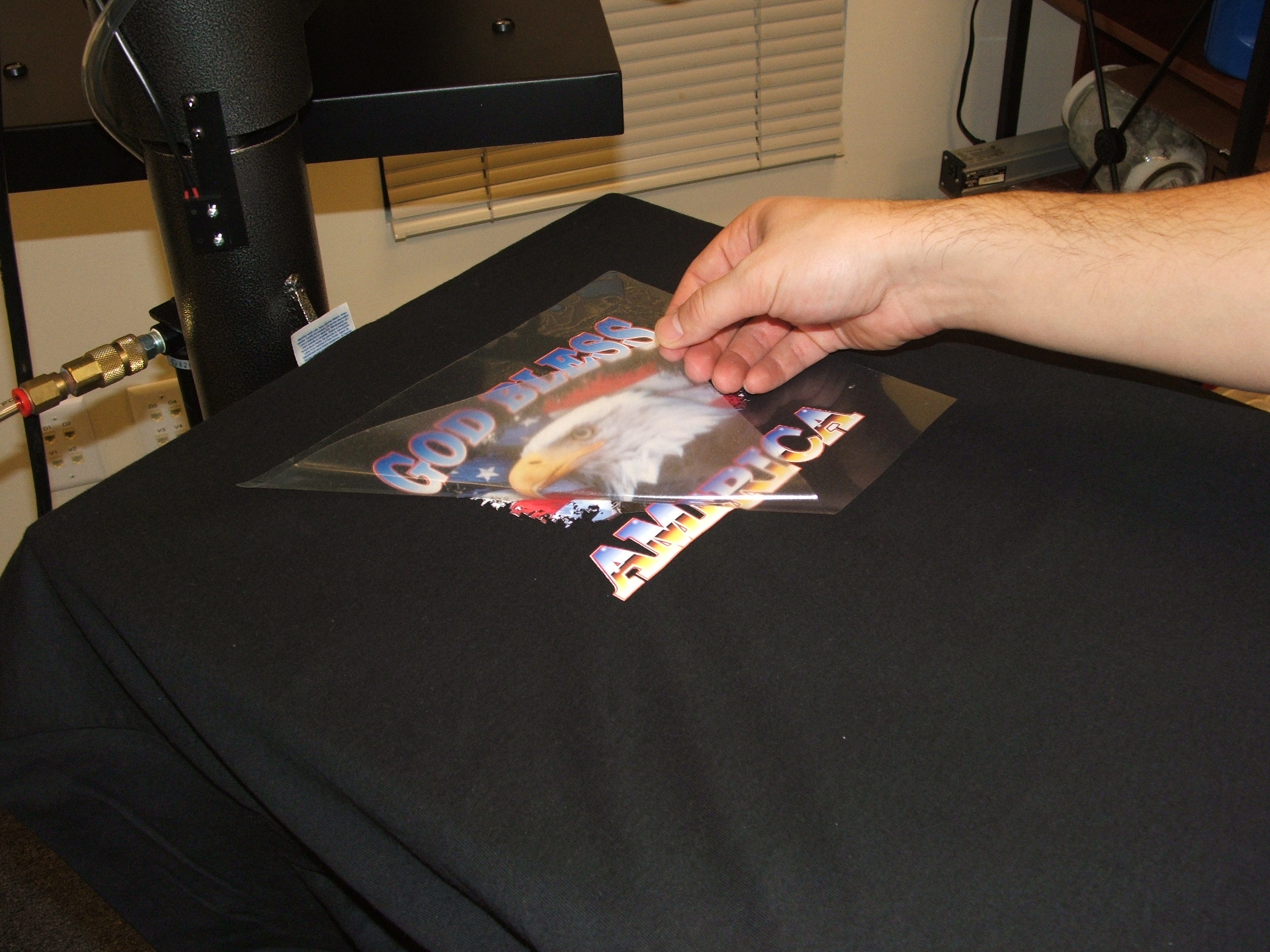


2. Heat Transfer Printing
How it works:
Designs are printed onto transfer paper, then heat-pressed onto fabrics. Uses either sublimation (dye turns to gas) or thermoplastic (ink melts onto material).
Pros:
Vibrant colors, works on multiple materials (textiles, ceramics, metal), and durable prints.
Cons:
Energy-intensive, size-limited, color-matching challenges, and high setup costs for complex designs.
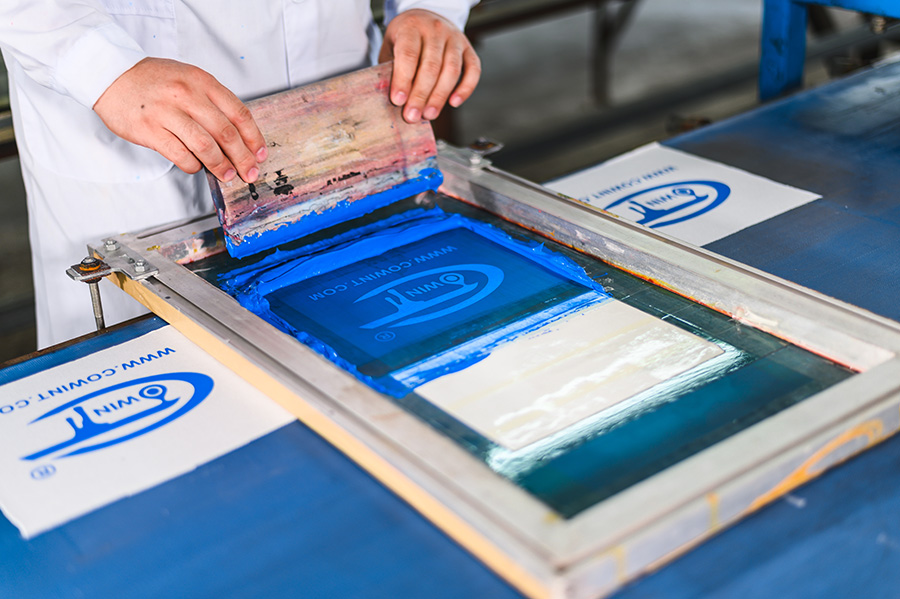
3. Plastisol Printing
How it works:
It is one of the common screen printings as we normally know.
A polymer-based ink is pushed through stenciled screens onto fabric, forming a thick, opaque layer.
Pros:
Bold colors on dark fabrics, high durability, and wide fabric compatibility.
Cons:
Stiff texture, poor breathability, and struggles with fine details.


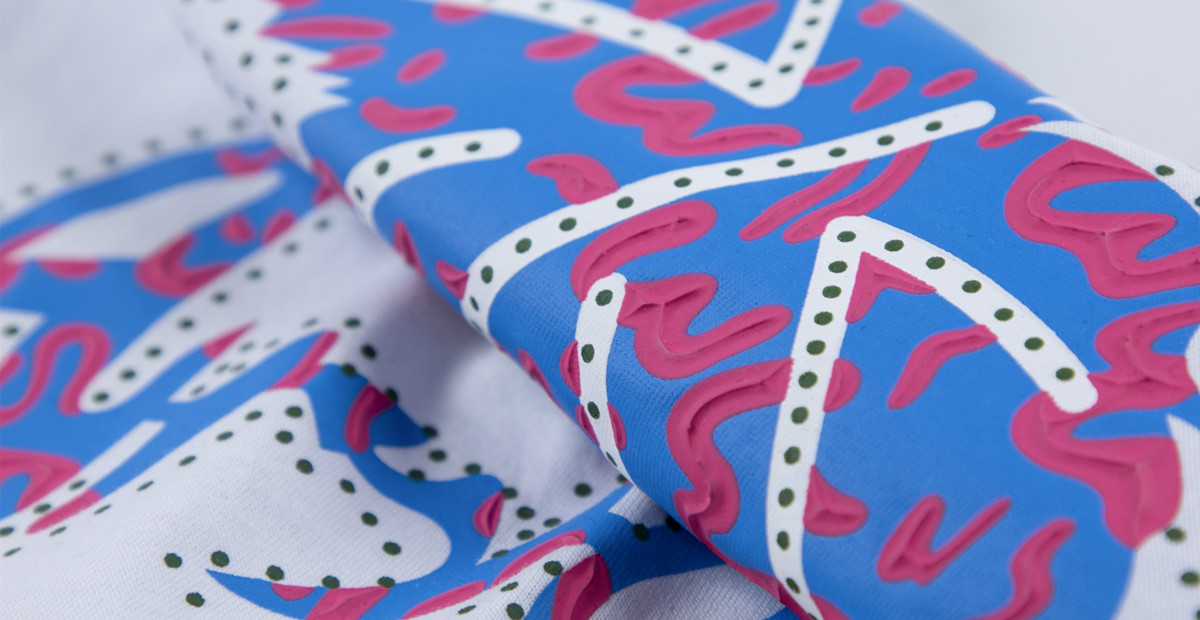
4. Raised Rubber Printing
How it works:
Special high-density ink is layered through screens to create raised, 3D patterns.
Pros:
Eye-catching texture, vibrant colors, and strong durability.
Cons:
Rigid feel, poor flexibility (cracks on stretchy fabrics), and slow production.
5. Puff Printing
How it works:
Ink mixed with foaming agents expands when heated, creating soft, puffy designs.
Pros:
Unique 3D effects, comfortable texture, and versatile colors.
Cons:
Prone to cracking, heat-sensitive, and inconsistent sizing.


6. Discharge Printing
How it works:
Chemicals remove dye from pre-colored fabrics, revealing lighter patterns.
Pros:
Soft finish, vintage aesthetic, and high precision.
Cons:
Complex process, fiber damage risks, and color limitations.
7. Crackling Printing
How it works:
Special shrinking inks create intentional cracks as they dry, mimicking a weathered look.
Pros:
Artistic distressed effects, soft texture, and good wash resistance.
Cons:
Technically demanding, slow production, and material limitations.


8. Drag (Pull Paste) Printing
How it works:
Combines dye removal and re-coloring to create contrasting patterns on pre-dyed fabrics.
Pros:
High-contrast designs, intricate details, and soft fabric feel.
Cons:
Labor-intensive, limited color options, and high skill requirements.
9. Flocking Printing
How it works:
Electrostatically charged fibers (flock) adhere to adhesive-coated fabric areas, creating a velvety texture. Excess fibers are vacuumed away after curing.
Pros:
Luxurious 3D texture, soft touch, diverse color options, sound-absorbing/thermal properties.
Cons:
Poor abrasion resistance, difficult cleaning, high material/equipment costs, slow production.


10. Water-based Printing
How it works:
Water-soluble inks penetrate fabric fibers via screens, ideal for lightweight designs.
Pros:
Soft hand feel, breathable, vibrant colors, eco-friendly.
Cons:
Weak opacity on dark fabrics, fading after washes, limited detail precision, slow drying.
11. Reflective Printing
How it works:
Glass beads or micro-prisms embedded in ink reflect light for visibility in low-light conditions.
Pros:
Enhances safety (night visibility), modern aesthetic, durable under gentle care.
Cons:
High material costs, limited viewing angles, muted color palette.

12. Silicone Printing
How it works:
Silicone-based ink is screen-printed and heat-cured to form flexible, glossy designs.
Pros:
Durable 3D effects, stretch-resistant, weatherproof, non-toxic.
Cons:
Stiff texture, reduced breathability, expensive inks, slow curing.
13. Thermo-chromic Printing
How it works:
Heat-sensitive inks change color when exposed to temperature shifts (e.g., body heat).
Pros:
Interactive "magic" effects, creative branding tool, functional for temperature indicators.
Cons:
Fades over time, limited activation range, high ink costs, UV-sensitive.
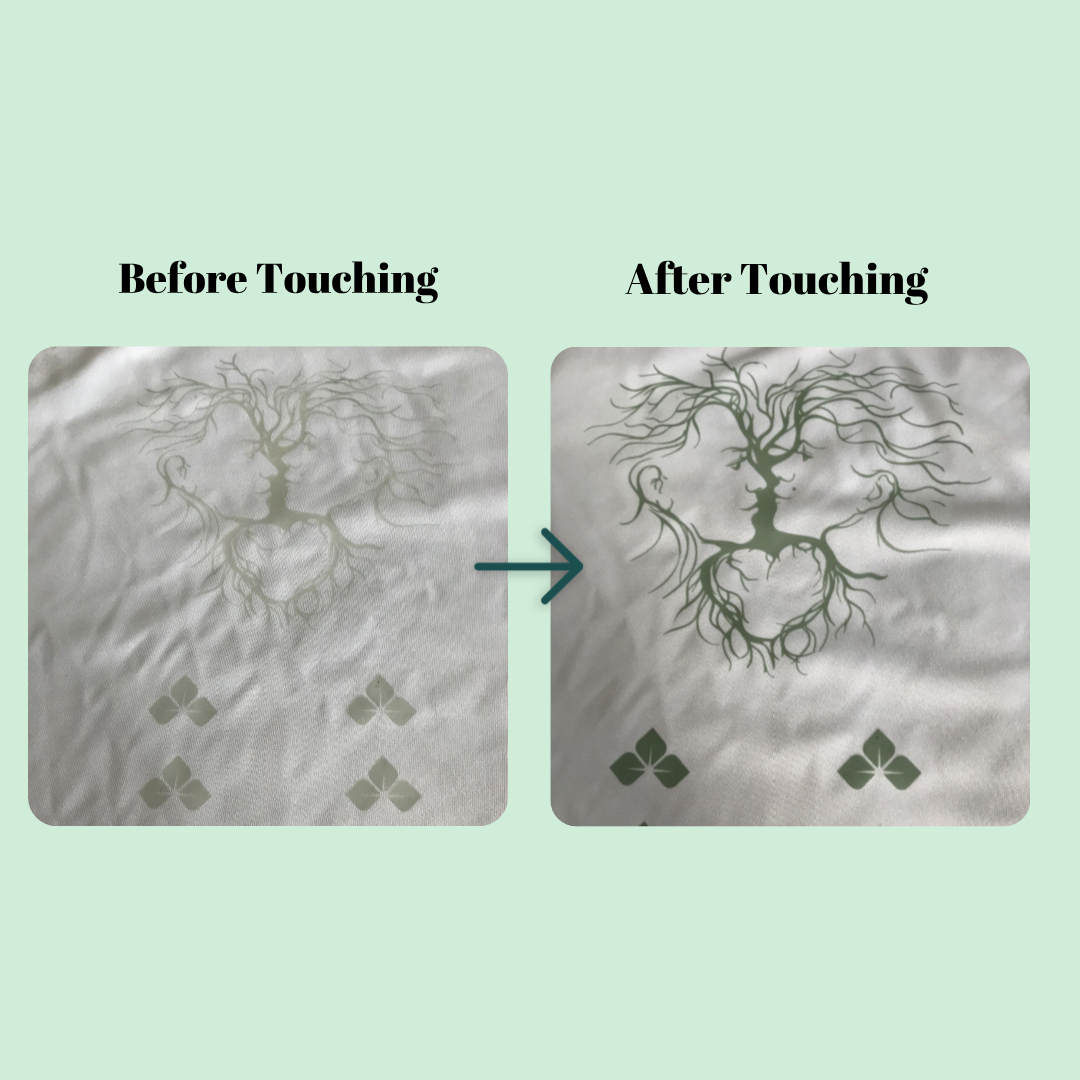

14. 3D Embossing Printing
How it works:
A steel die presses patterns into fabric under heat/pressure, creating permanent 3D textures.
Pros:
Bold tactile finishes, ultra-durable, industrial-chic appeal.
Cons:
High die setup costs, inflexible designs, works best on rigid fabrics, risk of fabric damage.
15. Ink Printing
How it works:
Pigmented or dyed ink is applied to fabrics, paper, plastics, or leather using printers or manual tools. The ink bonds to the substrate through physical/chemical adhesion, forming a stable film after drying.
Pros:
Vivid versatility: Achieves nearly any color with photorealistic precision.
Fine details: Perfect for intricate patterns, text, or high-resolution imagery.
Broad compatibility: Works on fabrics, plastics, leather, and more.
Cons:
Stiff feel: Creates a rigid texture on soft materials like clothing.
Poor breathability: Ink layers may trap heat and moisture.
Durability issues: Prone to fading or peeling with frequent washing/sun exposure.
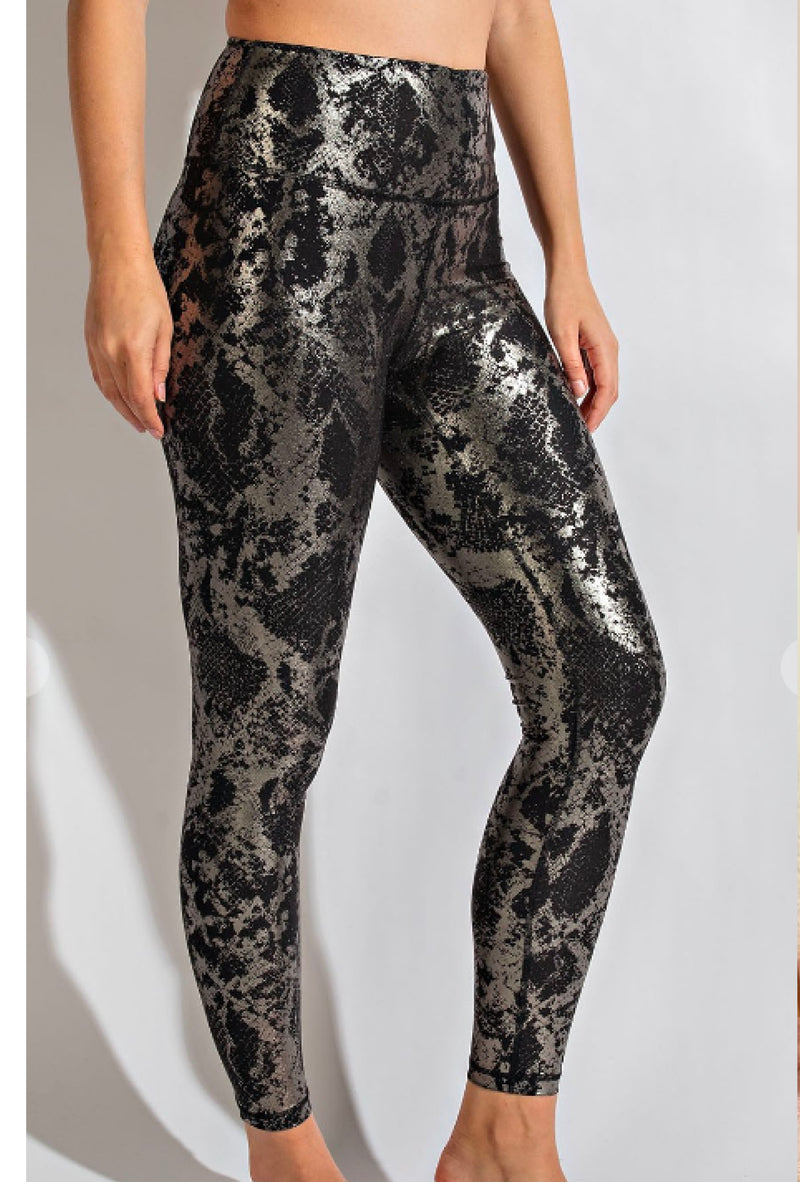


16. Hot Foil Printing
How it works:
Heat and pressure transfer metallic foil layers from a carrier sheet to substrates. The foil’s adhesive melts under heat, bonding to the material permanently.
Pros:
Luxury appeal: Adds metallic shine (gold, silver) for premium aesthetics.
Durability: Resists scratches, fading, and wear under normal use.
Multi-material use: Applies to fabrics, paper, plastics, and leather.
Cons:
High costs: Foil materials and specialized equipment raise production expenses.
Limited colors: Primarily metallic shades; colored foils are rare and costly.
Texture trade-off: Foil areas feel stiff, reducing fabric softness.
As a clothing manufacturer, Arabella is keen to provide you versatile product resolutions for our clients. And sharing is one of our way to learn. So, here are some of printings that so far we sharing with you and we would like to learn more. Feel free to let us know if you have any other confusion during the way you are exploring your clothing business. We will be here for you. ;)
Stay tuned and we will get back soon with more latest news!
https://linktr.ee/arabellaclothing.com
info@arabellaclothing.com
Post time: Mar-07-2025
